As with humans, a strong immune system is vital for fish to maintain good health. When the immune system is weakened, the body does not function well and one tends to be prone to illness. If so, recovering from illness is even harder. Let’s take a look at a scientific approach to why this is the case.
Omega-3 and omega-6 balance
To a large extent, the difference between good health and disease is about the ratio between the number of cells which work well, and those that do not. The cells have many functions, such as signaling, transporting, fighting, building and protecting, and the balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids is important for their ability to perform these tasks.
Read more: Five fun facts - on krill
Where are they formed?
Only marine organisms are a rich source of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-6s on the other hand are primarily formed in land plants.
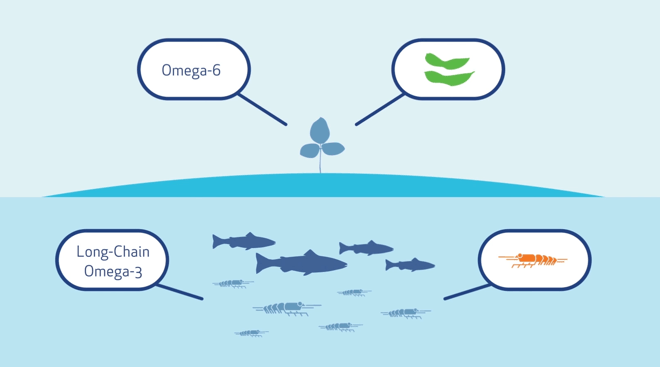
Long chained omega-3's are often marinebased vs omega-6 is often plantbased.
Omega-3s and Omega-6s have important but different jobs
The cell membrane is responsible for the ability of the cell to communicate with the surrounding world. It controls the passage of substances. Omega-3s contribute to the cell having a flexible and permeable membrane helping to give the right signals.
For optimal health and the capacity to resist disease, fish need a responsive immune system. Inflammation is the body's way of saying that something is wrong and that the immune system should start to fight the intruder, like a virus or infection.
Omega-6 fatty acids are important for fish to activate the immune system. When the immune system has done its job, omega-3 fatty acids are needed to reduce inflammation.
Read more: Ensuring the low impact on the Antarctic system
Short film on the fish immune system:
In order to strengthen the immune system, the balance between the two fatty acid forms is decisive. Too much omega-6s can lead to more inflammation, whereas omega-3s have anti-inflammatory effects.
It is important that fish have access to both, but in order to manage inflammation and infection efficiently, they require the right balance.
Studies have shown that by eating krill, fish develop stronger heart muscles and healthier circulatory systems. This results in lower mortality and less disease, as well as improved fillet quality.

